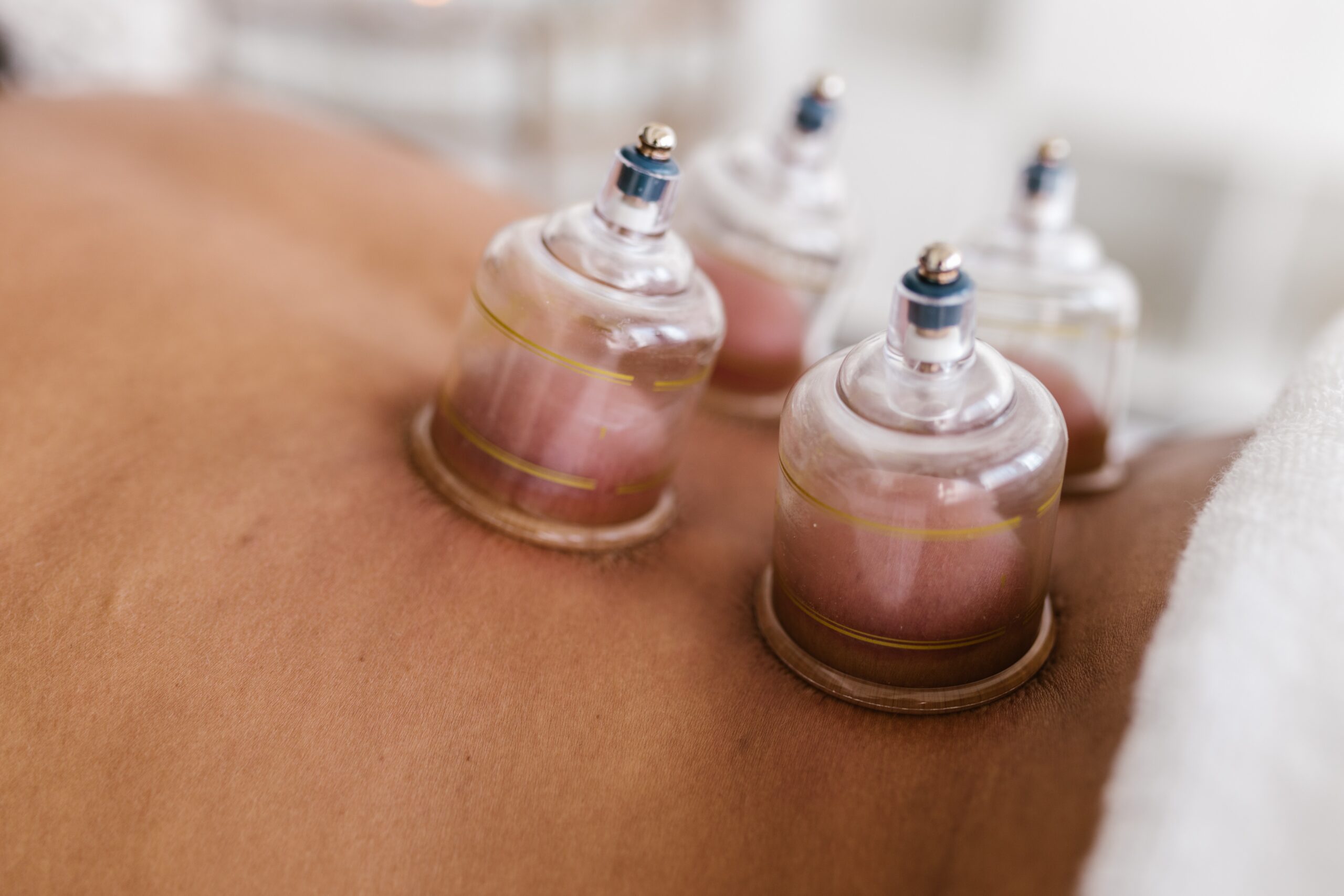
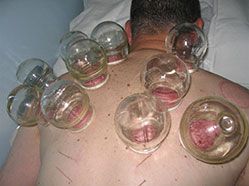
Cupping refers to an ancient Chinese practice in which a cup is applied to the skin and the pressure in the cup is reduced so that the skin and superficial muscle layer is drawn into and held in the cup. In some cases, the cup may be moved while the suction of skin is active, causing a regional pulling of the skin and muscle (the technique is called gliding cupping).
Cupping is applied by acupuncturists to certain acupuncture points, as well as to regions of the body that are affected by pain. When the cups are moved along the surface of the skin, the treatment is somewhat like gua sha (scraping). This is for the intention of breaking stagnation.
In some cases, a small amount of blood letting is done first using a pricking needle, and then the cup is applied over the site. This technique is said to promote blood circulation, remove stasis, and alleviate swelling and pain. It is employed especially when there is a toxic heat (such as shingles) syndrome and for a variety of acute ailments.
The glass cups are depressurized by providing some fire in the cup to heat up the air within just prior to placement. A cotton ball is dipped in alcohol with a pincer, ignited then held in the cup and quickly applied to the skin.
Generally, the cup is left in place for about 5-15 minutes. The skin becomes reddened due to the build up of wind, cold and damp and stagnation of blood and qi flow. Some bruising along the site of the rim of the cup is expected or where the cups are. The bruising will usually subside between 3-5 days depending on the severity of the condition. It is the body’s response way of detoxifying.
Cupping may be used for relieving tension, muscular aches and pains, gastro-intestinal disorders, skin conditions, lung diseases, gynaecological disorders and paralysis. The areas of the body that are fleshy are preferred sites for cupping.
Effects
- Improves Circulation of Qi & Blood
- Removes Wind, Cold & Dampness
- Reduces Toxicity
- Relieves Muscle Tension
- Non Invasive